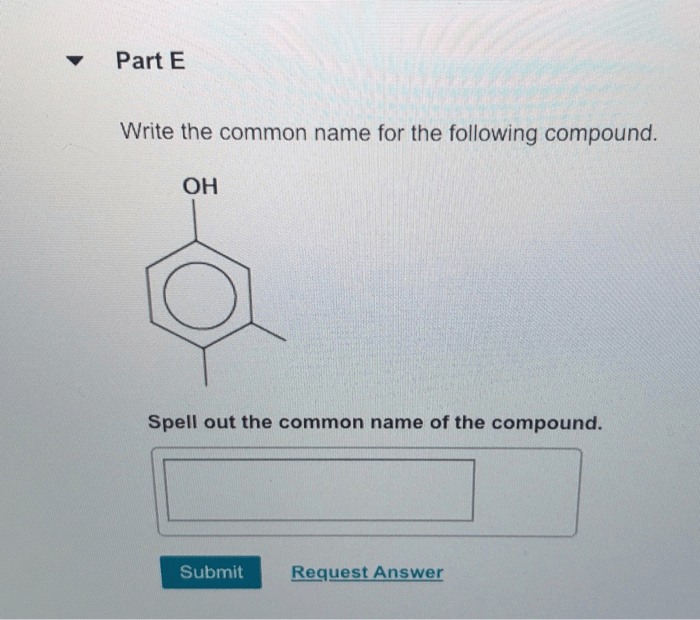
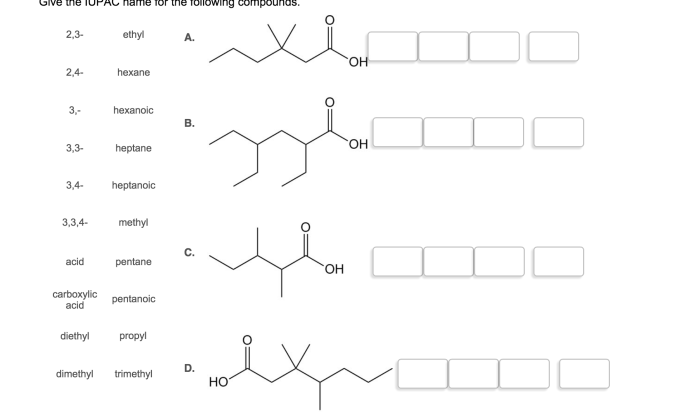
Spell out the IUPAC name of the compound embarks on an enlightening journey into the world of chemical nomenclature, unveiling the principles and practices that govern the systematic naming of organic compounds. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, providing a roadmap for navigating the complexities of chemical structures and assigning them precise and unambiguous names.
Delving into the fundamentals of IUPAC nomenclature, we explore the underlying principles that guide the construction of compound names. By understanding the significance of functional groups, identifying the parent chain, and mastering the art of numbering carbon chains, we lay the groundwork for deciphering the intricate tapestry of organic molecules.
IUPAC Nomenclature Fundamentals
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a set of guidelines for naming organic compounds in a systematic and unambiguous manner. This nomenclature system is essential for clear and consistent communication in scientific research and applications.
Principles of IUPAC Nomenclature
- Compounds are named based on their structure and functional groups.
- The longest continuous carbon chain is identified as the parent chain.
- Substituents attached to the parent chain are named and incorporated into the IUPAC name.
- The IUPAC name is constructed in a specific order: parent chain, substituents, functional groups.
Importance of IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature ensures that scientists worldwide can understand and communicate about chemical structures clearly and consistently. It facilitates the sharing of research findings, the development of new compounds, and the safe handling and use of chemicals.
Identifying Functional Groups: Spell Out The Iupac Name Of The Compound
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that impart characteristic chemical properties. They influence the IUPAC name of a compound.
Common Functional Groups
- Alkanes (CnH2n+2): No functional groups
- Alkenes (CnH2n): C=C double bond
- Alkynes (CnH2n-2): C≡C triple bond
- Alcohols (ROH): -OH hydroxyl group
- Aldehydes (RCHO): -CHO carbonyl group
- Ketones (RCOR’): -CO- carbonyl group between two alkyl groups
- Carboxylic acids (RCOOH): -COOH carboxyl group
IUPAC Prefixes and Suffixes for Functional Groups
| Functional Group | Prefix | Suffix |
|---|---|---|
| Alkene | Alken | -ene |
| Alkyne | Alkin | -yne |
| Alcohol | Hydroxy | -ol |
| Aldehyde | Oxo | -al |
| Ketone | Oxo | -one |
| Carboxylic acid | Carboxy | -oic acid |
Determining the Parent Chain
The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. It forms the backbone of the IUPAC name.
Rules for Selecting the Parent Chain
- Identify all continuous carbon chains in the molecule.
- Select the chain with the most carbon atoms.
- If there are multiple chains with the same number of carbon atoms, choose the chain with the most branches.
Examples of Determining the Parent Chain, Spell out the iupac name of the compound
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3: Parent chain is pentane (5 carbon atoms)
- CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH3: Parent chain is pentane (5 carbon atoms, more branches than CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3)
- CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3: Parent chain is pentane (5 carbon atoms, more branches than CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3)
Numbering the Carbon Chain
Carbon atoms in the parent chain are numbered sequentially, starting from one end and proceeding to the other. This numbering determines the location of substituents and functional groups.
Rules for Numbering the Carbon Chain
- Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain so that the substituents and functional groups have the lowest possible numbers.
- If there are multiple substituents or functional groups on the same carbon atom, assign the lowest number to the group with the higher priority.
- In case of a tie, give priority to the group that appears first in the IUPAC nomenclature order.
Examples of Numbering Carbon Chains
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3: Carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5, starting from either end.
- CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH3: Carbon atom with the methyl group is numbered 2, and the remaining carbon atoms are numbered 1, 3, 4, and 5.
- CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3: Carbon atom with the methyl group is numbered 3, and the remaining carbon atoms are numbered 1, 2, 4, and 5.
Naming Substituents

Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain. They influence the IUPAC name of the compound.
IUPAC Prefixes for Substituents
| Substituent | Prefix |
|---|---|
| Methyl | Methyl |
| Ethyl | Ethyl |
| Propyl | Propyl |
| Butyl | Butyl |
| Pentyl | Pentyl |
| Hexyl | Hexyl |
Incorporating Substituents into the IUPAC Name
Substituents are incorporated into the IUPAC name by adding their prefixes before the parent chain name. The location of the substituent is indicated by the number of the carbon atom it is attached to.
Examples of Naming Substituents
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3: Pentane
- CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH3: 2-Methylpentane
- CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3: 3-Methylpentane
Putting it All Together
To construct the complete IUPAC name, combine the information from the previous steps:
Order of Writing the IUPAC Name
- Parent chain name
- Substituents, in alphabetical order
- Functional groups, in order of priority
Examples of Spelling Out IUPAC Names
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3: Pentane
- CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH3: 2-Methylpentane
- CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3: 3-Methylpentane
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH: 1-Pentanol
- CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-OH: 3-Methyl-1-pentanol
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a systematic and universally recognized method for naming organic compounds, ensuring clear and unambiguous communication among chemists.
How do functional groups influence IUPAC names?
Functional groups are key structural features that determine the IUPAC name of a compound. They are assigned specific prefixes or suffixes that reflect their presence and connectivity within the molecule.
What is the role of the parent chain in IUPAC nomenclature?
The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain in the compound. Its identification forms the foundation for constructing the IUPAC name and incorporating substituents.
