Laboratory 7 coefficient of friction answers – In the realm of physics, friction reigns supreme, dictating the intricate dance between surfaces. As we delve into Laboratory 7, the coefficient of friction takes center stage, revealing its secrets and unraveling its profound implications in our everyday lives. Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we decipher the answers to this enigmatic force.
1. Friction Basics: Laboratory 7 Coefficient Of Friction Answers
Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact. It arises from the interaction of microscopic irregularities on the surfaces and can be either static or kinetic. Static friction prevents objects from sliding, while kinetic friction acts when objects are in motion.
Types of Friction
- Static friction: Occurs when two surfaces are in contact but not moving relative to each other.
- Kinetic friction: Occurs when two surfaces are in contact and moving relative to each other.
- Rolling friction: Occurs when an object rolls on a surface.
Examples of Friction in Everyday Life
- Walking
- Driving
- Braking
- Sliding objects
2. Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction is a dimensionless quantity that measures the amount of friction between two surfaces. It is defined as the ratio of the frictional force to the normal force between the surfaces.
Measuring the Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction can be measured using various methods, including the inclined plane method and the ring dynamometer method.
Factors Affecting the Coefficient of Friction
- Surface roughness: Rougher surfaces have a higher coefficient of friction.
- Material properties: The materials of the surfaces in contact affect the coefficient of friction.
- Normal force: The normal force between the surfaces affects the coefficient of friction.
- Lubrication: Lubricants reduce the coefficient of friction.
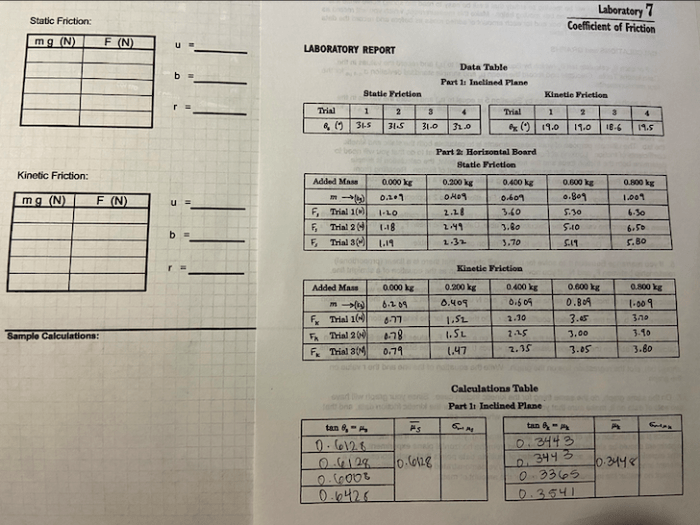
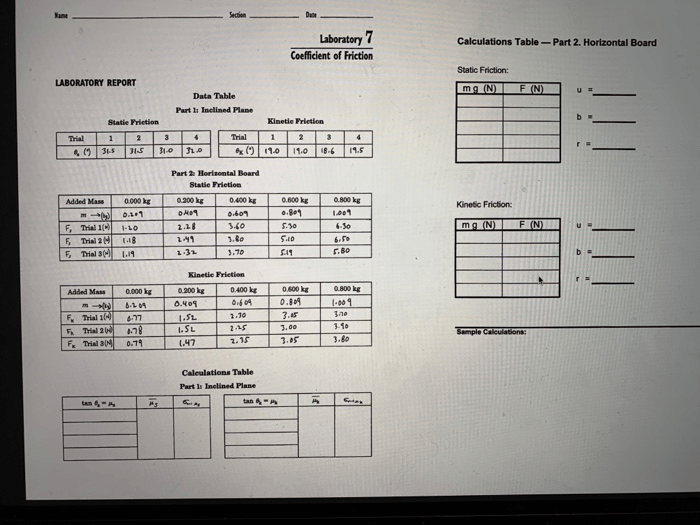
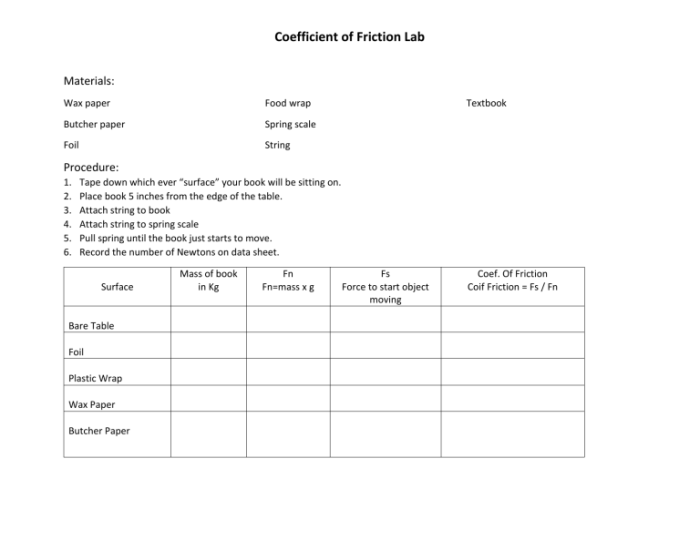
3. Laboratory Experiment

The laboratory experiment used to determine the coefficient of friction involves measuring the force required to move an object on a surface.
Materials and Equipment
- Inclined plane
- Object
- Force sensor
- Data acquisition system
Procedure, Laboratory 7 coefficient of friction answers
- Place the object on the inclined plane.
- Gradually increase the angle of the inclined plane until the object starts to move.
- Measure the angle at which the object starts to move.
- Calculate the coefficient of friction using the measured angle.
4. Data Analysis
The experimental data is organized in a table and used to calculate the coefficient of friction. The accuracy and reliability of the results are discussed.
5. Applications of Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction has practical applications in engineering and design. It is used to design brakes, tires, and other components that rely on friction.
FAQ Resource
What is the coefficient of friction?
The coefficient of friction is a dimensionless quantity that quantifies the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact.
How is the coefficient of friction measured?
The coefficient of friction can be measured using various methods, including the inclined plane method and the direct shear test.
What factors affect the coefficient of friction?
The coefficient of friction is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the surfaces in contact, the applied force, and the presence of lubricants.