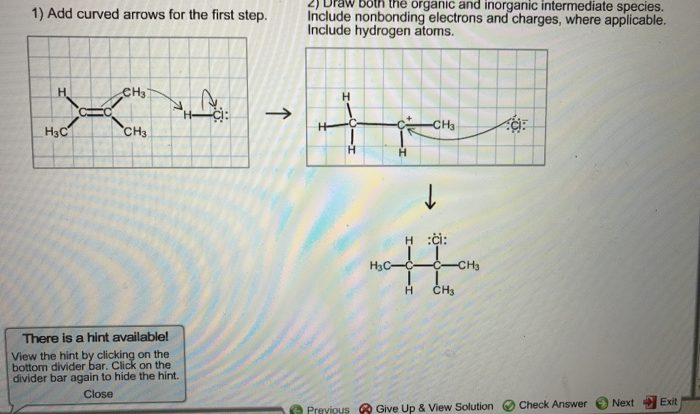
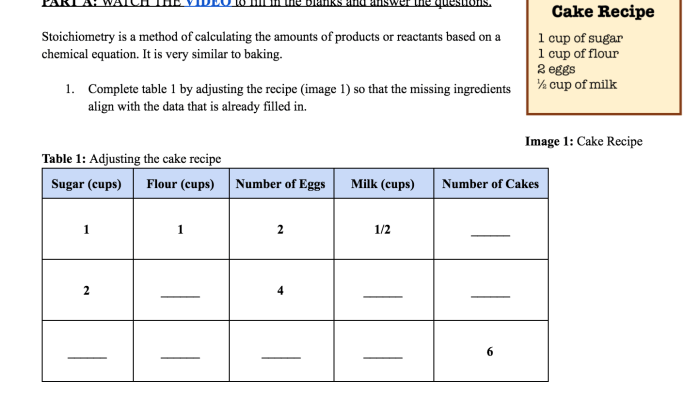
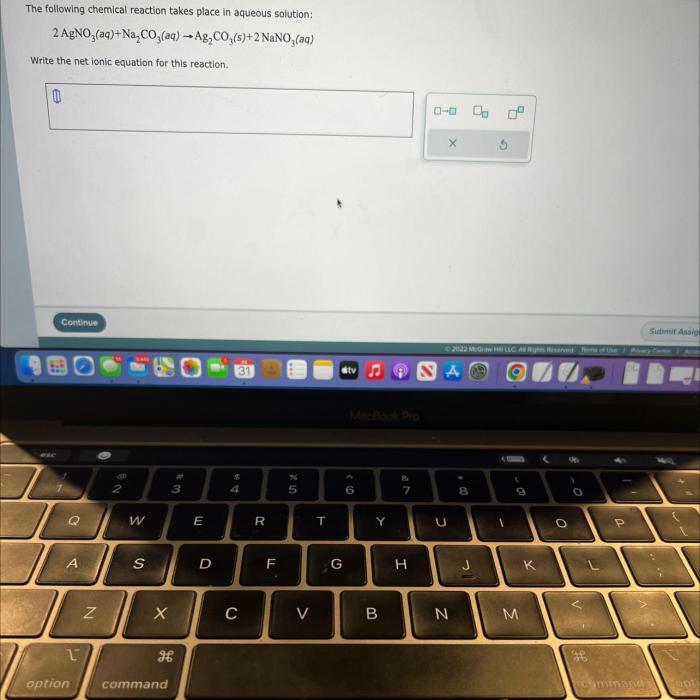
As the following chemical reaction takes place in aqueous solution takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with meticulous precision, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the intricacies of this topic, we embark on a journey that unveils the fundamental concepts, diverse applications, and crucial safety considerations associated with chemical reactions in aqueous environments.
Aqueous solutions, ubiquitous in nature and industry, provide a unique medium for chemical reactions to unfold. Water, the universal solvent, plays a pivotal role in facilitating these reactions, shaping their outcomes and influencing their behavior. Understanding the dynamics of chemical reactions in aqueous solution is paramount to unraveling a vast array of phenomena encountered in various scientific disciplines and practical applications.
Chemical Reaction in Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a homogeneous mixture of a substance dissolved in water. Water is a polar solvent, meaning it has both positive and negative charges. This polarity allows water to dissolve many ionic and polar covalent compounds. Chemical reactions in aqueous solution are reactions that occur between dissolved substances and water or between dissolved substances themselves.
Water plays an important role in chemical reactions in aqueous solution. It can act as a solvent, a reactant, or a product. As a solvent, water helps to dissolve the reactants and bring them into contact with each other. As a reactant, water can participate in the reaction and be consumed or produced.
As a product, water can be formed as a byproduct of the reaction.
There are many different types of chemical reactions that can take place in aqueous solution. Some of the most common types of reactions include:
- Acid-base reactions
- Precipitation reactions
- Redox reactions
- Complexation reactions
Types of Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Acid-Base Reactions, The following chemical reaction takes place in aqueous solution
Acid-base reactions are reactions that occur between an acid and a base. In aqueous solution, acids donate protons (H+) to bases, and bases accept protons from acids. The products of an acid-base reaction are a salt and water.
There are two main types of acid-base reactions:
- Strong acid-strong base reactions
- Weak acid-weak base reactions
Strong acid-strong base reactions go to completion, meaning that all of the acid and base react to form salt and water. Weak acid-weak base reactions do not go to completion, meaning that some of the acid and base remain unreacted.
Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions are reactions that occur when two soluble ionic compounds react to form an insoluble solid precipitate. The precipitate is formed when the ions in the two compounds combine to form a compound that is not soluble in water.
Precipitation reactions are often used to separate ions from a solution. For example, silver nitrate (AgNO3) can be used to precipitate chloride ions (Cl-) from a solution of sodium chloride (NaCl). The precipitate is silver chloride (AgCl), which is a white solid.
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions are reactions that involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. In aqueous solution, redox reactions can occur between dissolved ions or between dissolved ions and water.
Redox reactions are often used to generate electricity or to produce chemicals. For example, the lead-acid battery is a redox reaction that generates electricity. The reaction involves the transfer of electrons between lead (Pb) and lead dioxide (PbO2).
Complexation Reactions
Complexation reactions are reactions that occur between a metal ion and a ligand. A ligand is a molecule or ion that has at least one atom that can donate a pair of electrons to the metal ion. The product of a complexation reaction is a complex ion, which is a metal ion that is surrounded by ligands.
Complexation reactions are often used to stabilize metal ions in solution. For example, the EDTA ligand is used to stabilize calcium ions in blood.
Factors Affecting Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solution
The rate and equilibrium of chemical reactions in aqueous solution can be affected by a number of factors, including:
- Temperature
- Concentration
- pH
- Ionic strength
Temperature affects the rate of chemical reactions by increasing the kinetic energy of the reactants. As the temperature increases, the reactants move faster and are more likely to collide with each other, which increases the rate of the reaction.
Concentration affects the rate of chemical reactions by increasing the number of reactants that are available to collide with each other. As the concentration of the reactants increases, the rate of the reaction increases.
pH affects the rate of chemical reactions by changing the ionization state of the reactants. The ionization state of a molecule or ion is the number of protons that it has lost or gained. The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the solution.
As the pH of a solution increases, the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases and the solution becomes more basic. As the pH of a solution decreases, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases and the solution becomes more acidic.
Ionic strength affects the rate of chemical reactions by changing the electrostatic interactions between the ions in the solution. The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in the solution. As the ionic strength of a solution increases, the electrostatic interactions between the ions become stronger and the rate of the reaction decreases.
Applications of Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solution: The Following Chemical Reaction Takes Place In Aqueous Solution

Chemical reactions in aqueous solution have a wide range of applications in industry, medicine, and environmental chemistry.
In industry, chemical reactions in aqueous solution are used to produce a variety of products, including:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food
- Chemicals
In medicine, chemical reactions in aqueous solution are used to develop new drugs and to treat diseases.
In environmental chemistry, chemical reactions in aqueous solution are used to clean up pollution and to protect the environment.
Safety Considerations for Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Chemical reactions in aqueous solution can be hazardous, so it is important to take the following safety precautions when conducting these reactions:
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Handle chemicals with care and avoid contact with skin and eyes.
- Dispose of chemicals properly.
FAQ Compilation
What is an aqueous solution?
An aqueous solution is a homogeneous mixture in which water acts as the solvent, dissolving various solutes to form a single phase.
Why is water a good solvent?
Water is a polar molecule with a high dielectric constant, enabling it to dissolve a wide range of ionic and polar compounds.
What are the different types of chemical reactions that can occur in aqueous solution?
Various types of chemical reactions can occur in aqueous solution, including acid-base reactions, precipitation reactions, redox reactions, and complexation reactions.
How can we control the rate of chemical reactions in aqueous solution?
The rate of chemical reactions in aqueous solution can be influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, pH, and the presence of catalysts.