Among the licensed drivers in the same age group – Driving safety among licensed drivers in the same age group presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. This comprehensive analysis delves into the age-specific driving statistics, risk factors, educational interventions, technological advancements, parental involvement, and cultural influences that shape driving behaviors in this demographic.
By exploring the similarities and differences between young drivers and their counterparts in other age groups, this study aims to identify effective strategies for improving safety on our roads.
Age-Specific Driving Statistics
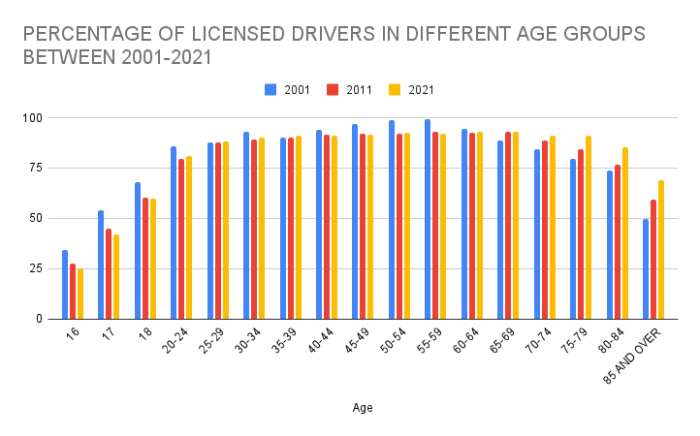
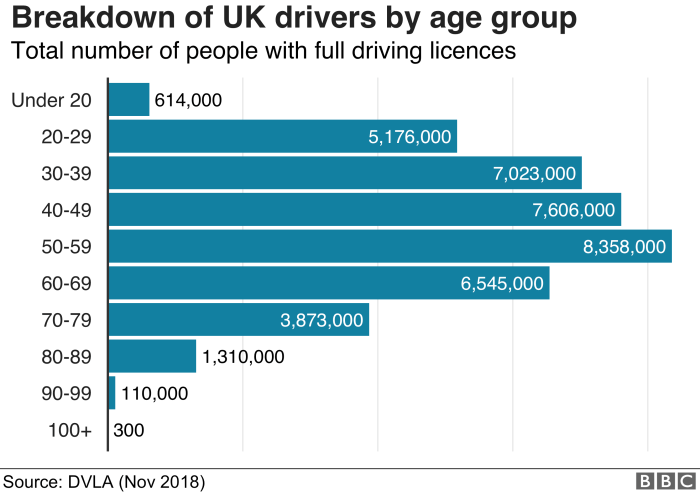
In the United States, there were approximately 221 million licensed drivers in 2021. Of these, drivers aged 16-24 years old comprised approximately 14.5%, representing a significant portion of the licensed driving population.
Compared to other age groups, young drivers aged 16-24 have a disproportionately high number of licensed drivers. They account for a higher percentage of licensed drivers than any other age group, with the exception of those aged 25-34.
Over the past decade, the number of licensed drivers in the 16-24 age group has remained relatively stable, with slight fluctuations from year to year.
Risk Factors and Safety Concerns
Young drivers aged 16-24 are at a higher risk of being involved in traffic accidents compared to other age groups. This increased risk is attributed to a combination of factors, including:
- Inexperience: Young drivers have less driving experience, which can lead to errors in judgment and decision-making.
- Cognitive Immaturity: Young drivers may have underdeveloped cognitive abilities, including attention, perception, and reaction time.
- Risk-Taking Behavior: Young drivers are more likely to engage in risky driving behaviors, such as speeding, reckless driving, and distracted driving.
- Peer Influence: Young drivers are more likely to be influenced by their peers, which can lead to unsafe driving practices.
- Substance Use: Young drivers are more likely to drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs, which significantly increases the risk of accidents.
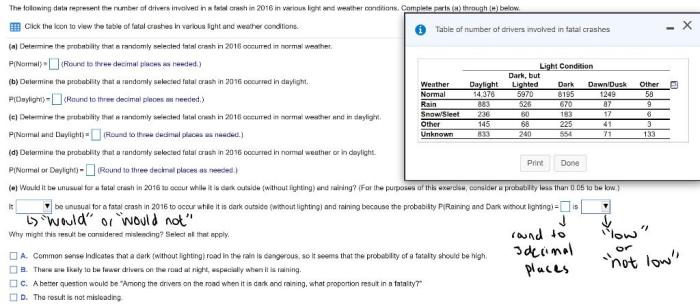
As a result of these risk factors, young drivers are involved in a disproportionate number of traffic accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), drivers aged 16-24 accounted for approximately 11% of all fatal crashes in 2020, despite representing only 14.5% of licensed drivers.
Educational and Intervention Programs
There are a number of educational and intervention programs aimed at improving driving safety among young drivers. These programs typically focus on:
- Providing information about traffic laws and safe driving practices.
- Developing skills in hazard recognition and risk assessment.
- Encouraging responsible decision-making and reducing risky driving behaviors.
- Promoting the use of seat belts and other safety features.
- Addressing the influence of peer pressure and substance use.
Research has shown that these programs can be effective in reducing traffic accidents and citations among young drivers. For example, a study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that a comprehensive driver education program reduced the risk of crashes among 16-19-year-old drivers by 20%.
Technological Advancements and Safety Features
Technological advancements have the potential to significantly improve driving safety for young drivers. These advancements include:
- Driver Assistance Systems (DAS): DAS can provide drivers with warnings, alerts, and automated interventions to help prevent accidents. Examples of DAS include lane departure warnings, forward collision warnings, and automatic emergency braking.
- Vehicle Safety Features: Vehicle safety features can help to reduce the severity of accidents. Examples of vehicle safety features include airbags, anti-lock brakes, and electronic stability control.
Research has shown that DAS and vehicle safety features can be effective in reducing traffic accidents and injuries. For example, a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that vehicles equipped with lane departure warnings had a 10% lower risk of being involved in a fatal crash.
Parental Involvement and Supervision
Parents play a critical role in promoting safe driving habits among young drivers. Parents can:
- Set clear rules and expectations for young drivers.
- Provide supervised driving practice.
- Talk to young drivers about the risks of unsafe driving behaviors.
- Model responsible driving behavior.
- Monitor young drivers’ driving records.
Research has shown that parental involvement can be effective in reducing traffic accidents and citations among young drivers. For example, a study by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety found that young drivers who had parents who set clear rules and expectations for driving were less likely to be involved in a crash.
Comparative Analysis of Different Age Groups: Among The Licensed Drivers In The Same Age Group
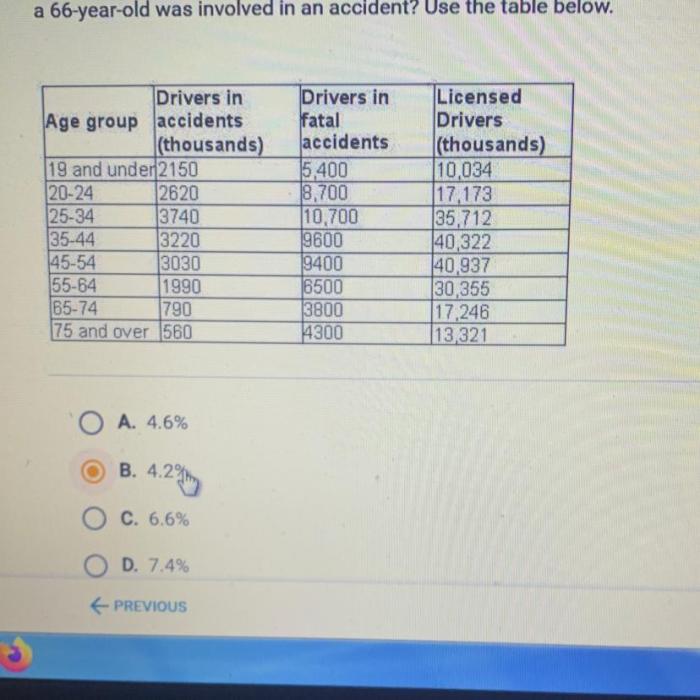
Compared to other age groups, young drivers aged 16-24 have a higher risk of being involved in traffic accidents. This increased risk is primarily due to the combination of inexperience, cognitive immaturity, and risky driving behaviors. As drivers age, their risk of being involved in an accident gradually decreases.
This is likely due to increased experience, improved cognitive abilities, and a reduction in risky driving behaviors.
However, it is important to note that young drivers are not the only age group at risk for traffic accidents. Drivers aged 65 and older also have a higher risk of being involved in fatal crashes. This increased risk is primarily due to age-related declines in cognitive abilities, vision, and reaction time.
Cultural and Societal Influences
Cultural and societal influences can also play a role in driving behaviors among young drivers. In some cultures, young drivers may be more likely to engage in risky driving behaviors due to peer pressure or a desire for independence. In other cultures, young drivers may be more likely to be cautious and responsible drivers due to strong family and community values.
It is important for parents, educators, and policymakers to be aware of the cultural and societal influences that can affect driving behaviors among young drivers. By understanding these influences, they can develop more effective strategies to promote safe driving habits.
FAQ
What are the unique risk factors associated with driving in this age group?
Young drivers are more likely to engage in risky behaviors such as speeding, texting while driving, and driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
How can educational programs and interventions improve driving safety among young drivers?
Educational programs that focus on safe driving practices, defensive driving techniques, and the consequences of risky behaviors can effectively reduce crash rates and improve overall safety.
What role do parents play in promoting safe driving habits among young drivers?
Parents can set clear rules and expectations, supervise their teens’ driving, and provide ongoing guidance and support to help them develop responsible driving habits.